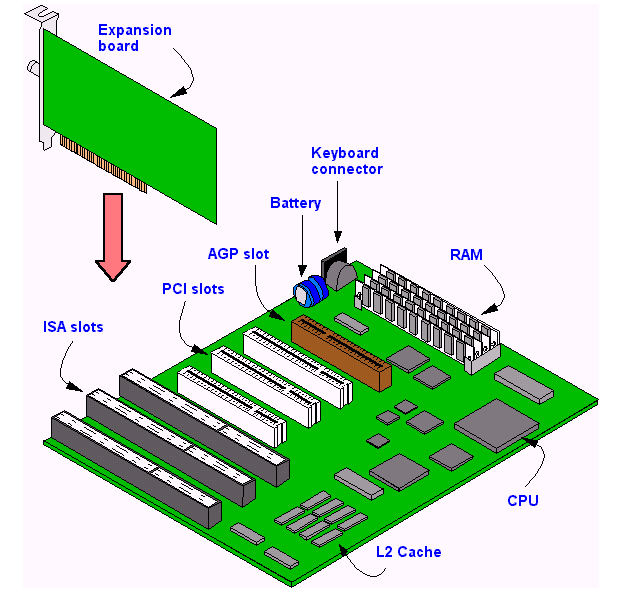
Expansion Slots Defined
PCMCIA is an acronym for Personal Computer Memory Card InternationalAssociation; the acronym is pronounced as separate letters. PCMCIA isa non-profit trade association and standards body consisting of some500 companies. PCMCIA has developed a standard for small, creditcard-sized devices, called PC cards, that are often used in notebookcomputers. (Adapters are available that allow PC cards to be used indesktop computer systems.) You can visit the PCMCIA web site at:
In the past, the cards were known as PCMCIA cards, but they are nowreferred to as PC cards, PC card hosts, and PC card software.PCMCIA refers to the association and standards body.
A PC card slot is an expansion slot often found in notebook computersthat allows for the easy and quick addition of a host of differentdevices. Originally designed for adding memory to portablecomputer systems, the PC card standard has been updated several timessince its original creation.
PC cards are Plug and Play devices that are often hot-swappable (i.e.,cards may be removed and inserted with the computer power turned on,without rebooting) under Mac OS and Windows 95and beyond. (Windows NT, however, has more limited supportfor PC cards, and you cannot change cards on the fly.) Many systemswill give a familiar beep sound from the computer's speaker when youremove or insert a card.
Differences between PC cards
AGP: Stands for 'Accelerated Graphics Port.' AGP is a type of expansion slot designed specifically for graphics cards. It was developed in 1996 as an alternative to the PCI standard. Since the AGP interface provides a dedicated bus for graphics data, AGP cards are able to render graphics faster than comparable PCI graphics cards. The PCI specifications define two different card lengths. The full-size PCI form factor is 312 millimeters long; short PCIs range from 119 to 167 millimeters in length to fit into smaller slots where space is an issue. Like the full-size PCI, the short PCI is a high-performance I/O bus that can be configured dynamically for use in devices with. If you’ve won free spins while playing a real-money slot, you have all chances What Is The Definition Of Expansion Slot to fatten up your bankroll. Every winning combination you land during free spins generates a real money profit. AGP slots were often colored maroon and had a hinged hook on one end to help anchor the AGP card. ISA: The original expansion slot for the PC family was ISA, which simply stood for Industry Standard Architecture (because the expansion slot lacked an official and suitably technical-sounding name). It had two varieties: 16-bit and a longer 16-bit.
There are three different types of PC cards. All three have the samerectangular size (85.6 by 54 millimeters), but different thicknesses.
- Type I cards can be up to 3.3mm thick, and are used primarily for addingadditional ROM or RAM to a computer.
- Type II cards (the most common) can be up to 5.5mm thick. Thesecards are often used for modem, fax, SCSI, andLAN cards.
- Type III cards can be up to 10.5mm thick, sufficiently large forportable disk drives.
Differences between PC card slots
As with the physical PC cards, PC slots also come in three sizes:

- A type I slot can hold one type I card
- A type II slot can hold one type II card, or two type I cards
- A type III slot can hold one type III card, or a type I and typeII card.
Most notebook computer systems come with two PC card slots that allowfor the use of two type I or type II PC cards and one type III PCcard. The PC card slots are stacked with one above theother. Usually, type III PC cards fit only in the bottom slot.
Common PC card devices
Following is a list of common PC card devices:
- CD-ROM interface
- Cellular phone interface
- Security tokens
- Docking station interface
- 10Mbps Ethernet LAN adapters
- 100Mbps Ethernet adapters
- GPS (Global Positioning System) cards
- Hard drives
- Infrared wireless LAN adapters
- ISDN cards
- Joystick interface cards
- Memory cards
- Modem and Ethernet combination cards
- Parallel port interface
- SCSI adapters
- Serial port interface
- Sound cards, input and output
- Video capture/frame grabber cards
- Video teleconferencing cards
Cardbus
Many laptop manufacturers now advertise their PC card slots as cardbuscompatible, or they simply identify the slots as cardbusslots. Cardbus is an extension of the latest PCMCIA standard, whichexpands the bus bandwidth and throughput to 32bits at 33MHz. In contrast, the older PC card standard was16 bits at 8MHz. Cardbus is analogous to the PCI slots in desktops,while the older PC card standard is analogous to ISA. The newercardbus slot can accommodate an older 16-bit PC card, but an older PCcard slot cannot accept newer cardbus cards. To tell if your PC cardis cardbus, look on the interface end of the card. Cardbus deviceswill have a notched metal plate on that end.
While not technically accurate, some vendors and technicians refer tothe older style 16-bit PC card as PCMCIA in order to contrast it with32-bit cardbus cards, which makes them sound like competingstandards. However, cardbus is an extension to the PCMCIA standard,not a replacement.
For additional information, see:
ExpressCard
The latest extension of the PCMCIA standard is calledExpressCard. This standard is being built on the latest USB2.0 and PCI Express buses. The aim is to increase speed and reducesize, cost, and complexity. One of the ways it does this is toeliminate the PCMCIA Host Controller in favor of using the USB or PCIExpress controller directly.
For additional information, see:

Summary :
Are you confused about PCI and PCIe? If you don't know how to distinguish them, you can read this post, in which MiniTool explains their differences to you from 4 aspects: function, appearance, speed, and compatibility.

Quick Navigation :
What Are PCI and PCI Express?
In the computer, if different devices want to exchange data, they must do that via a certain channel, that is, bus. Bus is a common communication trunk line for transmitting information between various functional parts of a computer. It is a transmission wiring harness composed of wires. Both PCI and PCIe are buses.
What Does PCI Do in a PC?
PCI is shorthand for Peripheral Component Interconnect, which is a local bus in PC. Then, how does it work in computers? I will explain that in this part.
Many years ago (around 2000-2010), the computer motherboard is constructed like the following picture:
Expansion Slots Defined Games
This structure is a typical North-South Bridge chip structure based on PCI bus. CPU and Northbridge chip are connected via FSB (Front Side Bus). The Northbridge chip is mainly responsible for controlling data exchange between CPU and high-speed devices (AGP graphics card, memory).
Then, Southbridge is connected to Northbridge via an internal bus (like Hub-Link). The Southbridge chip is mainly responsible for data exchange of low-speed devices like floppy drive, hard disk, keyboard, and add-in card.
Where is PCI? It's under Southbridge. Under Southbridge, there are many buses: PCI, LPC (Low Pin Count), SATA, USB, etc. PCI bus is mainly responsible for connecting devices like network card, audio card, and SCSI card. LPC bus is mainly responsible for connecting common low-speed devices like BIOS, keyboard, mouse, floppy disk, etc.
This article explains deeply what SATA SSD and M.2 SSD are. It touches upon SATA Bus standard, PCI-E Bus standard, AHCI protocol, and NVMe protocol.
What Does PCI Express Do in a PC?
Expansion Slots Define
What is PCI Express? PCI Express, also called PCIe/PCI-E, is the successor of PCI and AGP. In addition, it is gradually taking place of SATA and USB buses. A typical motherboard structure based on PCIe is shown like the following picture:
The above picture shows the structure of Intel Z390 motherboard that was launched at October 8, 2018. In this motherboard, Northbridge is totally integrated into CPU, so there are only two main parts: CPU and Southbridge (Intel calls it I/O Control Hub or Platform Controller Hub).
Similarly, the graphics card and memory are directly connected to CPU. But there are two points you should pay attention to: a. the graphics card is connected to CPU via PCIe bus; b. the motherboard supports direct connection between CPU and PCIe SSD.
Then, Intel Z390 chipset (Southbridge) is connected to CPU via DMI (Direct Media Interface) 3.0 bus that is based on PCIe bus. The Southbridge distributes 24 PCIe lanes used for connecting hard drives, USB devices, network card, audio card, etc. It can be said that PCIe is not just a local bus. It is already a system bus.
When you read here, you might be thinking 'where is my M.2 PCIe SSD plugged in?' Actually, there are two situations:

- Your graphics card uses PCIe 3.0 X8 lanes and other two PCIe 3.0 X4 ports are used to insert 2 NVMe SSDs. In this situation, the SSDs are connected to CPU directly, so that each of them can enjoy 4 GB/s throughput exclusively.
- Your graphics card uses PCIe 3.0 X16 lanes and your M.2 PCIe SSD shares 24 ICH/PCH PCIe lanes with other devices. In addition, the speed of SSDs will be limited by DMI 3.0 (the speed of DMI 3.0 X4 equals about that of PCIe 3.0 X4). That' why Thunderbolt 3, M.2, and U.2 interfaces are currently unable to break through the PCIeX4 bandwidth.
In most cases, your computer takes the second layout. Even though PCIe SSDs share throughput with other devices, they are still faster than other SSDs like SATA SSDs. Besides, the additional devices on the Southbridge will not operate all together usually, so the throughput of DMI 3.0 is sufficient.
This post introduces NVMe vs M.2 vs PCIe in detail. After reading this post, you can know the differences between them clearly.
PCI vs PCIe
In this part, I will explain PCI vs PCI Express from 3 aspects. Read on to learn about differences between PCI and PCIe further.
PCI vs PCIe Slot
In this part, I will show you what PCI and PCIe slots look like. The first one I will introduce is PCI slot. This slot has two types: 32-bit slot with 124 pins and 64-bit slot with 188 pins. The former is usually used in general desktop computers and the latter is generally used on servers. The PCI slot looks like the following picture:
Then, it's the turn to introduce PCIe slot. This slot has 7 versions: x1, x2, x4, x8, x12, x16, and x32, corresponding to 1/2/4/8/12/16/32 lanes, respectively. Among them, PCI-E x32 is only used in some special occasions due to its large size and there is almost no corresponding mass-production product.
PCI-E x12 is mainly used in servers and will not appear on consumer platforms. PCI-E x2 is mainly used for internal interfaces rather than expansion slots. Even if some motherboards provide this interface, PCI-E x2 basically appears in the form of M.2 interface instead of PCI-E slot.
Therefore, the mainstream PCI-E slots on the motherboard are basically concentrated on the four types: PCI-E x1 / x4 / x8 / x16. Let's introduce them in more detail:
- PCI-E x16 slot: It is 89mm long and has 164 pins. It is often used for graphics cards and backward compatible with x1 / x4 / x8 devices.
- PCI-E x8 slot: It is 56mm long and has 98 pins. It usually appears in the form of a PCI-E x16 slot, but only half of the data pins are valid, which means that the actual bandwidth is only half of the true PCI-E x16 slot. The purpose is to allow the graphics card with PCI-E x16 interface to be smoothly installed on the PCI-E x8 interface.
- PCI-E x4 slot: It is 39mm long and has 64 pins. It is mainly used for installing PCI-E SSDs or M.2 SSDs (through PCI-E adapters). But in most cases, the PCI-E x4 slot comes in the form of an M.2 interface when it leaves the factory.
- PCI-E x1 slot: It is only 25mm long and has 36 pins. The products targeted are relatively extensive, including independent network cards, independent sound cards, USB 3.0 / 3.1 expansion cards, etc.
Then, the PCI-E x1 / x4 / x8 / x16 slot looks like the following picture:
PCI vs PCIe Speed
In this part, I will explain PCI vs PCI-E speed. After learning about their speed differences, you will know why PCI interface is replaced by PCIe interface.
The 32-bit PCI speed is 133 MB/s, while the 64-bit PCI speed is 266 MB/s. As for PCIe speed, it varies depending on lanes and versions. Let's look at the PCIe performance diagram offered by Wikipedia:
At present, most computers use PCIe 3.0 version. With this version, even PCIe x1 can be much faster than 64-bit PCI. In terms of PCI vs PCI-E speed, PCI-E is winner and it totally takes the place of PCI.
Do you know what SSD drive is? This article will explain some SSD Terminologies and help you to fully understand SSD disk.
PCI vs PCIe Compatibility
In terms of compatibility, there are several points you should remember:
- PCI: The 32-bit PCI interface is not compatible with 64-bit PCI products, while the 64-bit PCI interface is compatible with 32-bit PCI products.
- PCIe: PCI-E interfaces have different lengths. The more lanes it has, the longer the interface. Generally, long slots are compatible with short interface products. For example, PCIe X16 slot can be compatible with X4 or X8 products. But short slots cannot be compatible with long interface products because they cannot be inserted.
- PCIe: PCIe has different versions. Different versions are compatible with each other. For example, PCIe 3.0 is compatible with PCIe 2.0. But the performance is determined by the low version.
- PCI vs PCIe: The PCI-E interface and the PCI interface are not compatible with each other.
Migrate Computer to PCIe SSD
After learning about PCIe vs PCI, you may want to use PCIe produces. If your computer has PCI-E interface, you can certainly enjoy the high speed of PCIe. In this part, I will show you how to migrate OS to a PCIe SSD with MiniTool Partition Wizard. In this way, you can use your PC on new hard drive without reinstalling OS.
This post provides a step-by-step guide on how to install a second hard drive in the laptop and desktop PC.
Here is the tutorial:
Step 1: Click the above button to buy MiniTool Partition Wizard. Install it and then open it to get its main interface. Click on Migrate OS to SSD/HDD in the toolbar.
Step 2: Choose the right method to migrate the system disk and click Next.
Option A: to replace the system disk with another hard disk: The entire system disk will be copied to the new SSD. The data includes system files and your personal files on other partitions.
Option B: to move operating system to another hard disk: Only the system and boot partitions required for OS are copied to the new SSD. Your personal files are still on the original disk.
Step 3: Choose the new SSD to migrate Windows to and click Next. A warning window will pop up. Read it and click Yes.
Step 4: Choose right copy options and adjust the target disk layout, and then click Next.
(1). Fit partitions to entire disk: All the partitions on the original disk are shrunk or extended by an equal proportion to fill the entire target disk.
(2). Copy partitions with resizing: All the partitions on the original disk are copied into the target disk without changes in size or location.
(3). Align partitions to 1 MB: It is recommended for improving computer performance.
(4). Use GUID partition table for the target disk: MBR can only recognize and use 2TB disk space at most. This option can convert MBR to GPT, thus users can use the disk space beyond 2 TB.
Step 5: Read the note and click Finish, then click Apply on the toolbar to execute the pending operations.
Step 6: MiniTool Partition Wizard will ask for a reboot. Click Restart Now.
Bottom Line
Has this post helped you learn about PCI vs PCIe? Do you have any opinions about PCI and PCIe? Please give us feedback in the following comment zone. Besides, if you have difficulty in migrating OS to PCIe SSDs, you can contact us via [email protected]. We will reply to you as soon as possible.
PCI vs PCIe FAQ
Expansion Slots Types
Expansion Slots Definition